Understanding Thermal Ratings in Hollow Metal Doors: R-Value & U Value
When thermal performance shows up in door specifications, you’ll often see references to R-value and U-value. But what do they really mean? And how do they apply to hollow metal doors?
Let’s break it down in plain language.
 Why Thermal Ratings Matter in Hollow Metal Doors
Why Thermal Ratings Matter in Hollow Metal Doors
As energy codes tighten and sustainability goals grow, architects and specifiers are paying closer attention to how door assemblies impact the building envelope. Whether it’s for exterior openings in commercial buildings, conditioned corridors in hospitals, or hotel room doors, understanding thermal performance ensures compliance and comfort.
That’s where R-value and U-value come into play.
What’s the Difference Between R-Value and U-Value?
✅ R-Value: Resistance to Heat Flow
Think of R-value as a measure of how well a material resists heat transfer.
- Higher R-value = better insulation.
- It only measures the insulating material itself and not the entire door.
In hollow metal doors, R-value refers specifically to the insulating core (like polystyrene or polyurethane). For example:
- A polystyrene core might have an R-value around 5.
- A polyurethane core might be closer to 10, thanks to its superior insulating properties.
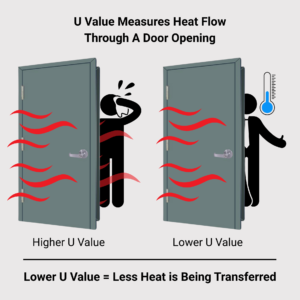
✅ U-Value: Rate of Heat Transfer
Now flip the perspective. U-value measures how easily heat flows through an entire assembly (including skins, edges, hardware preps, and seals).
- Lower U-value = better thermal performance overall.
Where R-value is a property of materials, U-value is a property of systems. It’s the number more often referenced in energy codes (like IECC) and certification programs (like LEED).
For a hollow metal door, the U-value accounts for heat transfer through the steel skins and any thermal bridging at edges or seams to give a more realistic picture of performance.
The Big Change: Why SDI Updated Thermal Testing
In the past, R-values were calculated using test methods that evaluated only a portion of the door—often ignoring frames, edges, and hardware. While this made for impressive numbers on paper, it didn’t reflect how doors perform in actual installations.
Enter the updated SDI 113 standard:
- The test method now evaluates the entire door and frame assembly under operable conditions.
- This means the resulting U-value represents true thermal performance—not just theoretical core insulation.
Why U-Value Matters More Than Ever
With stricter energy codes and growing sustainability goals, U-value is now the go-to metric for:
- IECC compliance
- LEED certifications
- Overall building envelope performance
Here’s a quick reference to keep in mind:
R-Value – Measures Core Insulation Only – Higher = Better Insulation
U-Value – Measure Opening Assembly – Lower = Better Thermal Barrier
Learn More
For more information on the updated testing methods and energy-efficient steel doors, visit: